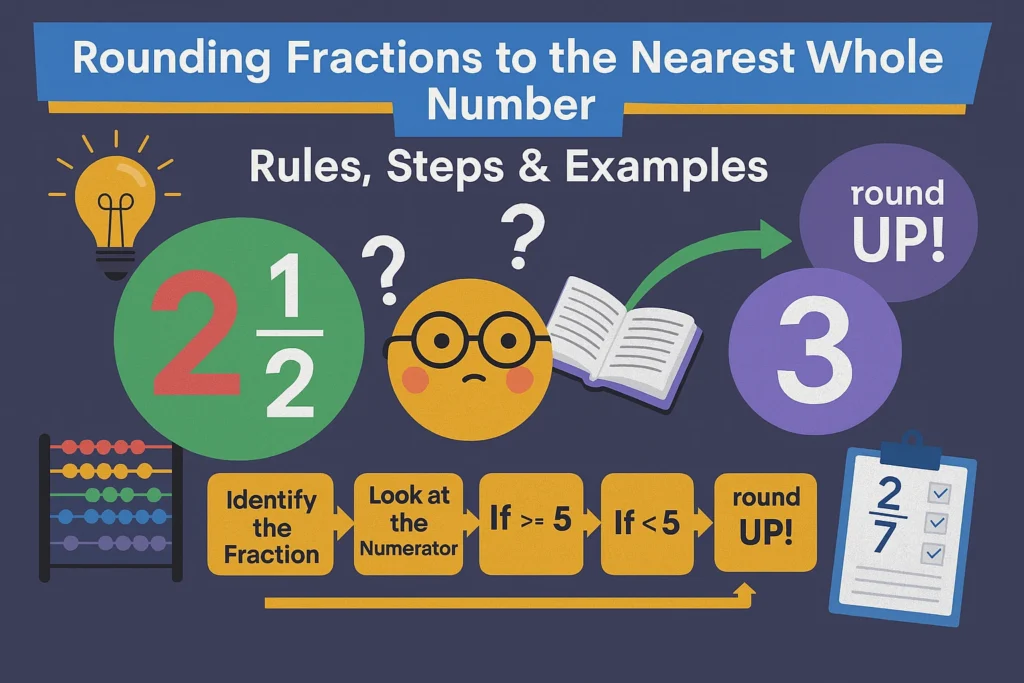
Rounding fractions is one of the easiest ways to simplify numbers for mental math, quick calculations, and classroom work. Instead of converting fractions into decimals every time, you can follow a simple set of rules to decide whether a fraction rounds down or up to the nearest whole number.
This guide explains rounding rules, gives clear steps, includes examples for all levels, and supports your main Rounding Fraction Calculator tool page with helpful, semantic content.
🔍 Quick Summary: When Do Fractions Round Up or Down?
- If the numerator is less than half of the denominator → Round Down
- If the numerator is equal to or greater than half → Round Up
This mirrors the same logic used when rounding decimals — just applied to fractions.
Why Rounding Fractions Matters
Students, teachers, and professionals use rounded fractions when:
- Estimating measurements
- Making quick calculations without a calculator
- Checking fraction answers for reasonableness
- Working with word problems
- Doing fast mental math in exams
How to Round Fractions to the Nearest Whole Number (Simple Rule)
Use this rule every time:
Step-by-Step Rule
- Compare the numerator to half of the denominator.
- If numerator < ½ denominator, round down.
- If numerator ≥ ½ denominator, round up.
- Write the result as a whole number.
Examples (From Easy to Trickier)
Example 1: 3/8
- Half of 8 = 4
- 3 < 4 → Round down
Answer: 0
Example 2: 5/6
- Half of 6 = 3
- 5 ≥ 3 → Round up
Answer: 1
Example 3: 7/10
- Half of 10 = 5
- 7 ≥ 5 → Round up
Answer: 1
Example 4: 15/32
- Half of 32 = 16
- 15 < 16 → Round down
Answer: 0
Example 5: 18/18
- Fraction equals 1
- Already a whole number
Answer: 1
Example 6: Mixed Fraction 2 7/12
- Half of 12 = 6
- 7 ≥ 6 → Fraction part rounds up → 1
- Whole number: 2
- 2 + 1 = 3
Answer: 3
How to Round Improper Fractions (Shortcut)
Turn the improper fraction into a mixed number, then apply the rounding rules to the fractional part.
Example: 17/9
- 17 ÷ 9 = 1 remainder 8 → 1 8/9
- Half of 9 = 4.5
- 8 > 4.5 → Round up
- Final: 2
Common Mistakes Students Make
✔ Comparing incorrectly (using denominator instead of half)
✔ Forgetting to convert improper fractions
✔ Rounding down when the fraction part is exactly ½
✔ Confusing rounding with simplifying fractions
When to Use the Rounding Fraction Calculator
Your calculator is helpful when:
- Fractions are large (e.g., 47/82)
- Mixed numbers become confusing
- Quick classwork checks are needed
- You want instant rounding + simplification
Need fast rounding? Try the Rounding Fraction Calculator for instant results.
FAQ
1. How do I round 1/2 to the nearest whole number?
Fractions that are exactly half, such as 1/2, 2/4, or 3/6, always round up to the next whole number.
2. What if the fraction is already a whole number?
If a fraction equals a whole number, such as 5/1 or 12/12, it stays the same and does not require rounding.
3. How do mixed numbers round?
To round mixed numbers, apply rounding rules only to the fractional part and add the result to the whole number.
4. Does simplifying affect rounding?
No — rounding works the same whether the fraction is simplified or not.
✅ Struggling with rounding? Learn the easiest way to round whole numbers in seconds.
✅ Easily convert fractions to decimals and decimals to fractions with step-by-step examples and powerful online calculator tools
✨ Confused by decimal places? Here’s the simplest way to understand tenths, hundredths, and thousandths.